Last week, simulation engineers and researchers from around the world tuned into the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America, our first ever online conference. Over the course of the event, attendees virtually presented their innovative simulation work, with topics ranging from acoustics modeling to bioengineering research to electromagnetics design. During the last hour of the two-day virtual conference, several attendees were recognized with Best Paper and Best Poster awards. Keep reading to get an overview of the award-winning work…
100+ Virtual Presentations Featuring a Variety of Industries
At the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America, 115 organizations and academic institutions showcased their unique simulation work using the COMSOL Multiphysics® software. Papers, posters, and prerecorded talks were given in five main categories:
- Multiphysics, Optimization, Particle Tracing, and Simulation Methods
- Structural Mechanics and Acoustics
- Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow
- Electromagnetics
- Chemical and Bioengineering
Among the many diverse user presentations, three papers were selected to win the Best Paper awards by the conference program committee and three posters were selected to win the Best Poster awards by popular vote from conference attendees.
“We greatly appreciate the work that is put into these presentations and for allowing us to share it with other engineers, researchers, and scientists across different industries,” said Dixita Patel, program chair for the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America. “It’s an honor being able to recognize and award our users for their contributions to the conference.”
3 Top Papers from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America
Analyzing the Famous Navier–Stokes Equations
The first Best Paper award went to Jim Freels and AJ Baker of the University of Tennessee, TN, for “Investigation of 1D Compressible Navier–Stokes Using Equation-Based Modeling”. The paper covers using equation-based modeling in COMSOL Multiphysics to explore the complex Navier–Stokes equations, which play a central role in fluid flow modeling.

Jim Freels accepting the Best Paper award from Phil Kinnane of COMSOL during the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America for “Investigation of 1D Compressible Navier–Stokes Using Equation-Based Modeling”. Screenshot taken in the GoToWebinar® platform.
In the future, the researchers plan to use the Application Builder in COMSOL Multiphysics to develop a simulation application from the models they discuss in their paper.
Improving MEMS Microphone Designs with Simulation
Thanks to microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology, silicon microphones are widely used in applications ranging from smartphones and tablets to automobiles. When compared to piezoelectric or piezoresistive microphones, silicon microphones have higher sensitivity and a lower noise floor, both considered advantages in microphone technology.
Shubham of Knowles Electronics received a Best Paper award for “Silicon Nitride Corrugated Membrane with High-Width-Aspect-Ratio for MEMS Microphones”. Shubham’s research discusses how to improve the acoustic sensitivity of a silicon MEMS microphone using a finite element modeling approach and analytical analysis. In order to do so, Shubham analyzed a MEMS microphone with a silicon nitride corrugated membrane (or diaphragm), paying close attention to the corrugation width.
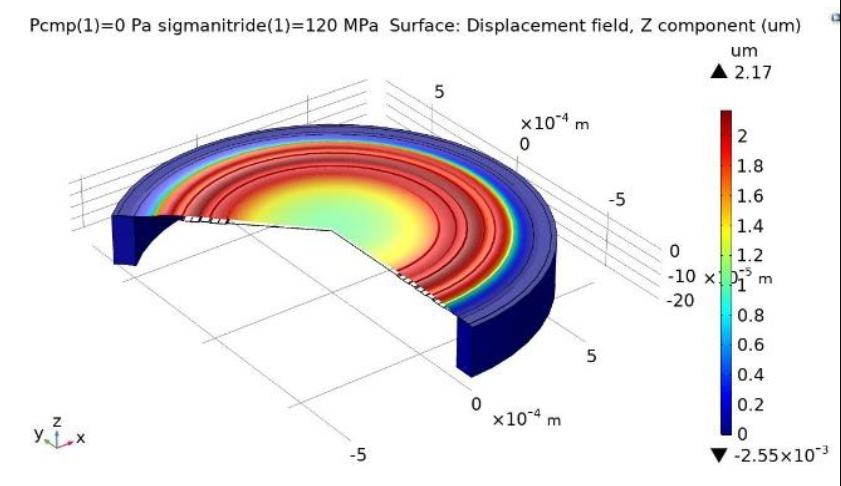
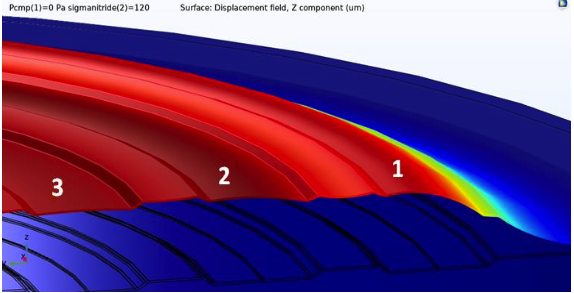
Simulation of the corrugated membrane (left) and a closeup view of the corrugated membrane (right). Images taken from the paper “Silicon Nitride Corrugated Membrane with High-Width-Aspect-Ratio for MEMS Microphones” from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America.
Modeling an Inductor with a Ferromagnetic Core
The final Best Paper award was presented to Alex Pokryvailo and Hiren Dave of Spellman-High Voltage for “Calculation and Measurement of Winding Loss at High-Frequency Pulsed Currents”. In their paper, Pokryvailo and Dave address that there are several sources that describe calculating copper losses in windings for high-frequency transformers and inductors. However, most of the existing work fails to recognize the winding aspect ratio and core presence of these components.
The pair used simulation to model and analyze an inductor with an open ferromagnetic core, a large winding curvature, and a high winding aspect ratio. In their work, they measured for a large variety of frequencies and current waveforms. They performed their simulations using COMSOL Multiphysics in the frequency domain and time domain.
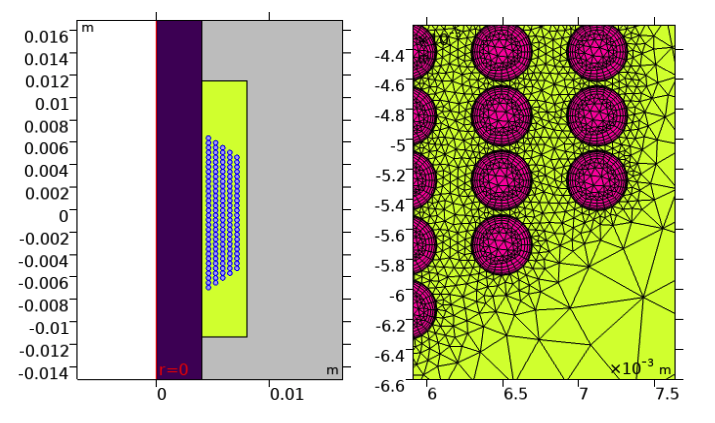
Geometry and mesh of the inductor. Image from the paper “Calculation and Measurement of Winding Loss at High-Frequency Pulsed Currents” from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America.
Favorite Posters from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America
COMSOL Conference attendees were able to vote for their favorite posters through the online conference dashboard. The following three projects were then awarded Best Poster awards at the end of the event.
PSA: COMSOL Conference attendees can vote for the best poster by visiting the Presentation Hall right from your conference dashboard! pic.twitter.com/MZe4XQwDyX
— COMSOL (@COMSOL_Inc) October 7, 2020
Modeling a Piezoelectric Transducer
In oncology, thermal ablation is often used to find primary and metastatic cancers through administered heating. Interstitial needle-based therapeutic ultrasound (NBTU) offers a minimally invasive approach when using thermal ablation. NBTU uses a piezoelectric transducer in order to produce localized heating at the target tumor location, which helps kill cancer cells.
Several researchers from Worcester Polytechnic Institute, General Electric Global Research, and Acoustics Medsystems Inc. were awarded a Best Poster award for “3D Thermo-Acoustic Modeling of a Piezoelectric Transducer for Directed Interstitial Ultrasound Ablation”. In their poster (shown below), the researchers describe how they set up a 3D simulation of a piezoelectric transducer for interstitial NBTU brain tumor ablation using COMSOL Multiphysics.
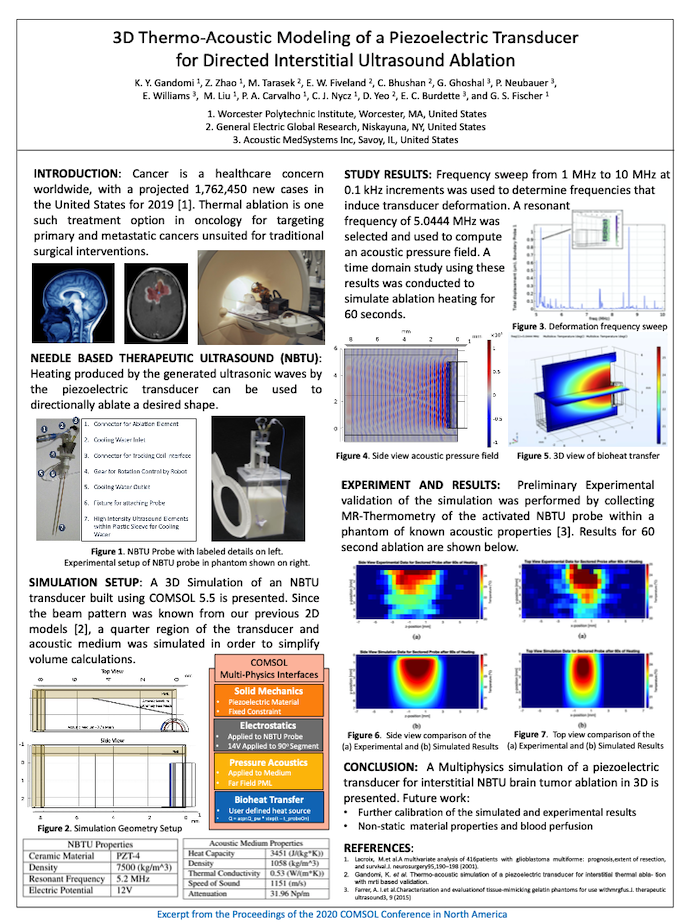
The “3D Thermo-Acoustic Modeling of a Piezoelectric Transducer for Directed Interstitial Ultrasound Ablation” poster from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America.
Using the simulation, they performed a resonant frequency and eigenmode analysis, acoustic pressure field frequency-domain study, and bioheat transfer time-domain study. In the future, they plan to create a 3D simulation of a rotating transducer and investigate its nonstatic material properties.
Investigating an Electrostatic Zipping Actuator
Researchers from the University of California and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) won a Best Poster award for their work entitled “Simulating Electrostatic Zipping Actuation in a Three-Chamber Peristaltic Micropump”. When compared to conventional electrostatic actuators, electrostatic zipping actuators offer certain advantages. For example, the latter has a specialized structure with small local gaps and offers a wide span of motion at lower applied voltages. Based on this knowledge of electrostatic zipping actuators, the researchers designed and analyzed an electrostatic zipping 3-chamber peristaltic micropump using simulation.
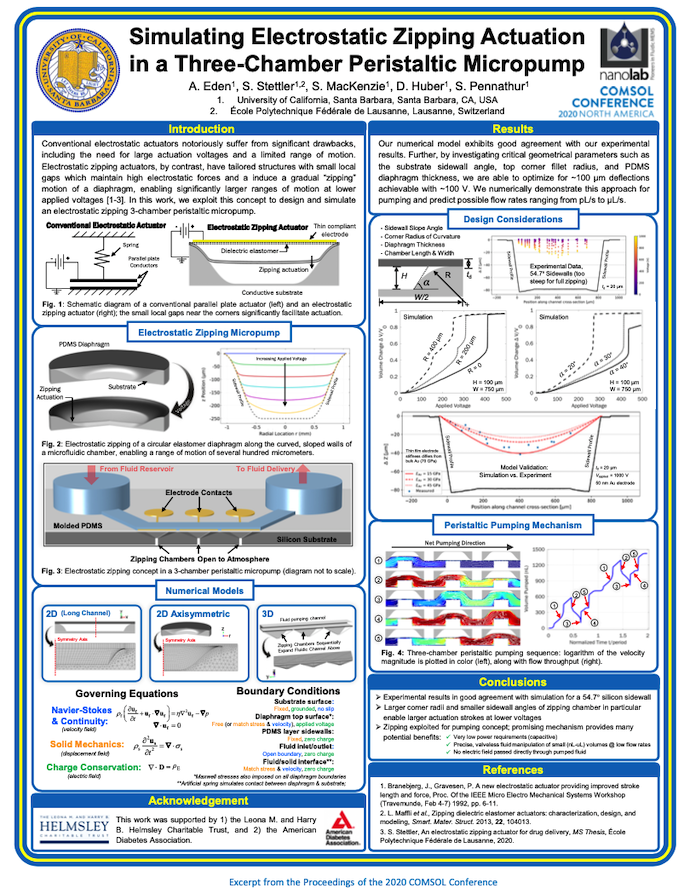
The “Simulating Electrostatic Zipping Actuation in a Three-Chamber Peristaltic Micropump” poster from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America.
Overall, the researchers found that their numerical model had good agreement with their experimental data. In addition, by modeling and analyzing the micropump’s important geometrical parameters (like the substrate sidewall angle and PDMS diaphragm thickness), the researchers were able to better understand its design and make improvements to it.
Studying Patient-Specific Models of Coronary Arteries
The final Best Poster award went to researchers from Stony Brook University and Cardiac Imaging, DeMatteis Center for Cardiac Research and Education, for their poster entitled “Fluid-Structure Interaction Studies of Coronary Artery Disease Biomechanics”.
Cardiovascular diseases are the number one cause of death worldwide. In the U.S., coronary artery disease is the most common form of heart disease. Computational models of coronary arteries can be used to investigate the development of atherosclerosis, or the buildup of plaque, in arteries, which can lead to coronary artery disease.
In their poster, the researchers highlight how they developed 2 models:
- 19-mm-long mesoscopic model of a diseased coronary artery, which contained a 70 percent stenosis
- 7.56-mm-long healthy coronary artery
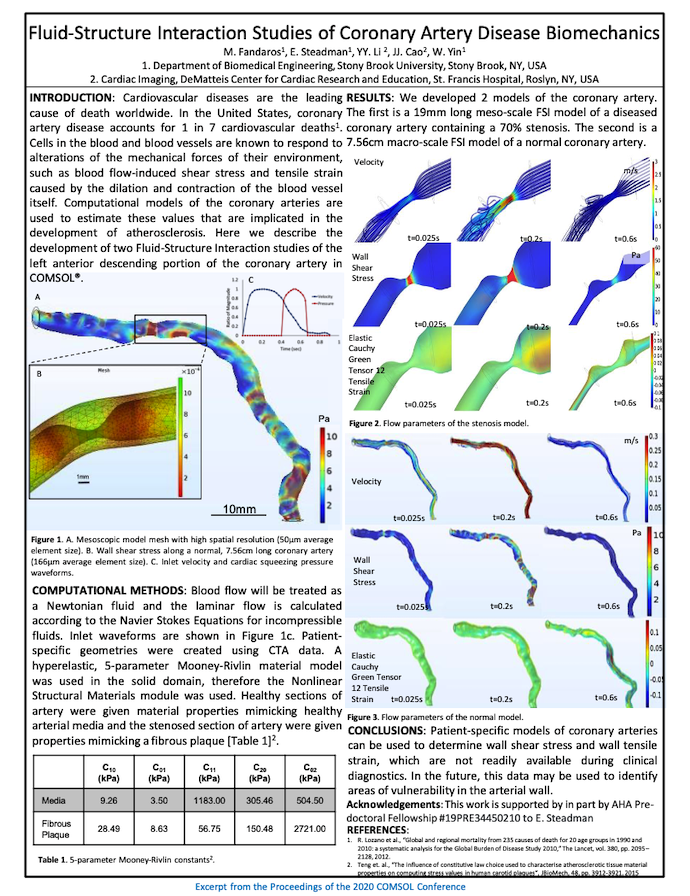
The “Fluid-Structure Interaction Studies of Coronary Artery Disease Biomechanics” poster from the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America.
Ultimately, the researchers found the simulation to be especially beneficial in analyzing the wall shear stress and wall tensile strain of the artery, both of which play a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
Thank You and Congratulations!
“Advanced, innovative, and inspirational,” said Program Chair Patel when asked to describe the user presentations in three words. “It’s interesting to see the research that is being conducted in both industry and academia and how each and every presentation is unique in its own way.”
Program Chair Dixita Patel presenting the Best Poster awards. Screenshot taken in the GoToWebinar® platform.
We would like to thank everyone who attended and presented their research at the COMSOL Conference 2020 North America and congratulate all of the Best Paper and Best Poster recipients. Your voices and ideas help shape the future of simulation technology, and we can’t wait to see what you do next.
GoToWebinar is a registered trademark of LogMeIn Inc.



Comments (0)