Heating Circuit
Application ID: 465
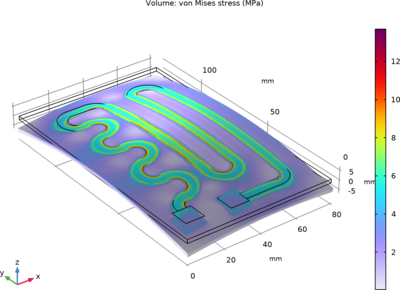
Small heating circuits find use in many applications. For example, in manufacturing processes, they heat up reactive fluids. The device in this tutorial example consists of an electrically resistive layer deposited on a glass plate. The layer results in Joule heating when a voltage is applied to the circuit, which results in a structural deformation. The layer’s properties determine the amount of heat produced.
This multiphysics example simulates the electrical heat generation, heat transfer, and mechanical stresses and deformations of a heating circuit device. The model uses the Heat Transfer in Solids interface in combination with the Electric Currents in Layered Shells interface and the Solid Mechanics interface. The Rigid Motion Suppression condition is automatically applied to a set of suitable constraints based on the geometry model and physics interfaces.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- Heat Transfer Module and
- either the AC/DC Module, or MEMS Module and
- either the MEMS Module, or Structural Mechanics Module
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



