Liquid–Liquid Extraction
Application ID: 114131
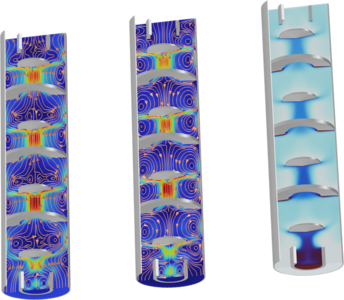
Liquid-liquid extraction is a process used to separate or transfer species between two immiscible liquids. Transfer of species from one phase to the other is driven by a difference in relative solubility. In this model a water filled extraction column is studied. Oil droplets containing a solute species are injected at the bottom of the column and rises up due buoyancy. As the oil droplets rise, the solute species is transferred into the aqueous phase. Water is injected at the top of the column. The column is fitted with a number of alternating horizontal discs in order to increase the residence time of the oil droplets.
The model is built using the Dispersed Two-Phase Flow with Species Transport multiphysics interface. The Mixture Model is used to compute the two-phase flow, where the k-omega model is used to account for the turbulent flow from the rising droplets. The species transport is solved for both in the continuous (water) phase and in the dispersed phase (oil droplets). Solute extraction is modeled using the Dispersed Two-Phase Flow, Diluted Species multiphysics feature.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



