Neutralization of Chlorine in a Scrubber
Application ID: 1401
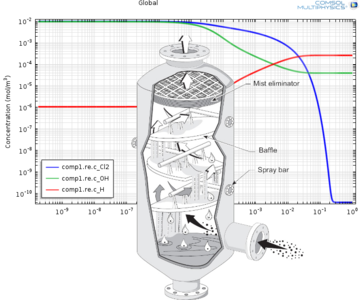
This example studies the kinetics of the neutralization of chlorine gas in water solution. The model assumes that the fluid volume is perfectly mixed and constant. This means that the chlorine has dissolved to an almost saturated state (1·10-2 mol/m3) and that the hydroxide has also mixed well throughout, as would be the case for a very small amount of fluid in a scrubber.
The study allows investigation of the time-scale of the reactions and the concentrations of the resulting products. A study of this type can be useful to determine the amount of hydroxide required to neutralize the chlorine and for sizing of a chlorine scrubber.
The model illustrates the usability of the Reaction Engineering interface available in the Chemical Reaction Engineering Module to study chemical processes involving several equilibrium reactions.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- either the Chemical Reaction Engineering Module, or Electric Discharge Module
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



