Power Transistor
Application ID: 8577
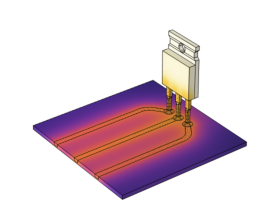
In every system where there is conduction of electric current, and where the conductivity of the material is finite, there will be electric heating. Electric heating, also referred to as Joule heating, is in many cases an undesired by-product of current conduction. This model simulates a system consisting of a small part of a circuit board containing a power transistor and the copper pathways connected to the transistor. The purpose of the simulation is to estimate the operating temperature of the transistor, which can be substantially higher than room temperature due to undesired electric heating. The power transistor, in this case an off-the-shelf product, can be mounted on a heat sink. However, in this simulation, we will investigate if heat sink mounting is necessary or if the operating temperature can be low enough to leave the system undamaged in the absence of a heat sink.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
