The Blasius Boundary Layer
Application ID: 13911
The incompressible boundary layer on a flat plate in the absence of a pressure gradient is usually referred to as the Blasius boundary layer. The steady, laminar boundary layer developing downstream of the leading edge eventually becomes unstable to Tollmien-Schlichting waves and finally transitions to a fully turbulent boundary layer.
Due to its fundamental importance, this type of flow has become the subject of numerous studies on boundary-layer flow, stability, transition, and turbulence.
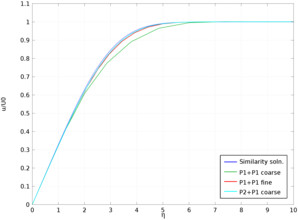
This model considers the first section of the plate where the boundary layer remains steady and laminar, and compares results from incompressible, two-dimensional, single-phase-flow simulations obtained in COMSOL Multiphysics to the Blasius similarity solution. The solutions converge ideally with respect to both mesh refinement and discretization order.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



