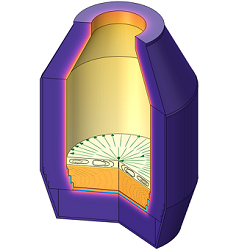
Top-blown rotary converter preheating and charge heating with an oxy-fuel burner
Present work is done in the framework of the SisAl Pilot EU project, which aims at optimising the silicon production in Europe by recycling materials and using a carbon-emission friendly technology. The silicon production experiments are conducted on laboratory and pilot scales in different types of furnaces, including top-blown rotary converters (TBRC) used as chemical reactors for molten slag-metal mixtures. Besides experimental work, the process optimisation also relies on the numerical modelling.
In this work COMSOL Multiphysics® is used for the numerical testing of a new thermal design of TBRC by simulating its preheating and charge heating in it due to an external heat source provided by an oxy-fuel burner. The risk of slag solidification in TBRC during aluminothermic reduction of silica was assessed. The following COMSOL® modules are employed: Heat Transfer in Solids and Fluids with phase change, Surface-to-Surface Radiation, and Turbulent Flow k-ω model to simulate the slag and metal flow. A bidirectional coupling of all the modules is present due to multiple interdependencies via material properties.
The model predicts that, with 600 kW of the useful burner power, the empty TBRC can be preheated up to 1650°C in less than 30 min. Thanks to the model, the optimum burner power for maintaining the TBRC charge in a liquid state is determined. The influence of TBRC inclination angle as well as of its rotation frequency is studied numerically. The presented modelling approach for testing new TBRC designs can be applied to other similar thermal problems.
Keywords: Top-blown rotary converter, Furnace preheating, Charge heating