Using the Shape Optimization Interface and Study Step
In this installment of our optimization course (Part 6 of 10), we start with an introduction to shape optimization, explaining what it is and providing an overview of the features and functionality in the COMSOL Multiphysics® software for performing this type of optimization. We discuss remeshing during optimization as well as the:
- Free Shape Domain feature
- Free Shape Boundary feature
- Free Shape Shell feature
- Polynomial Boundary feature
- Transformation feature (more on this in Part 10)
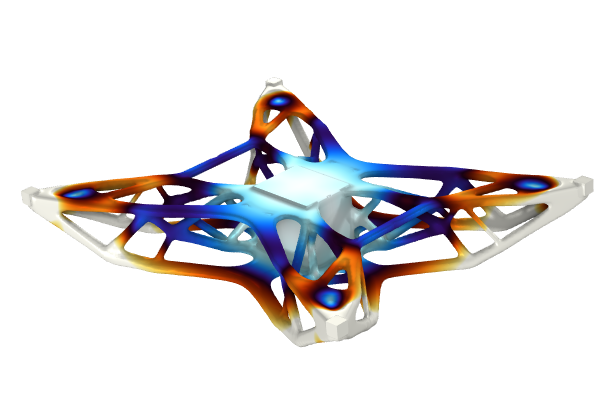
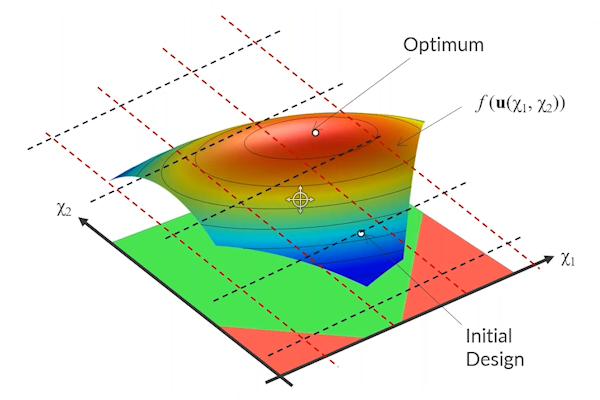
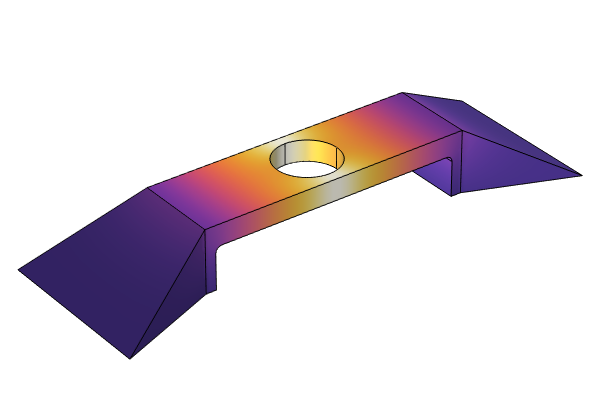
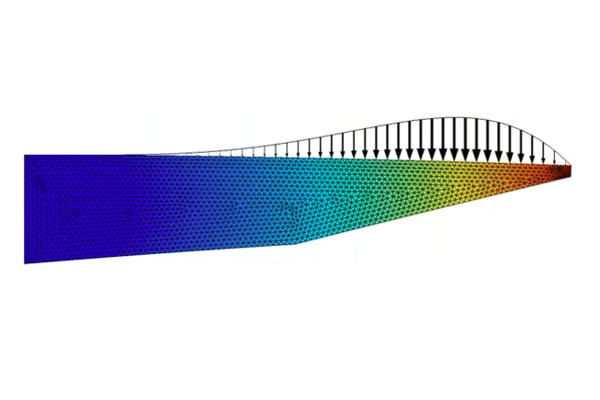
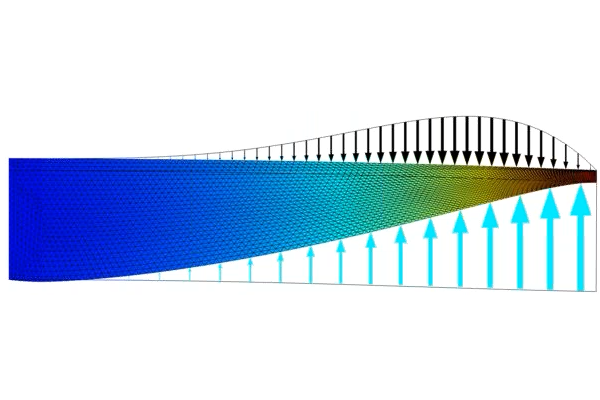
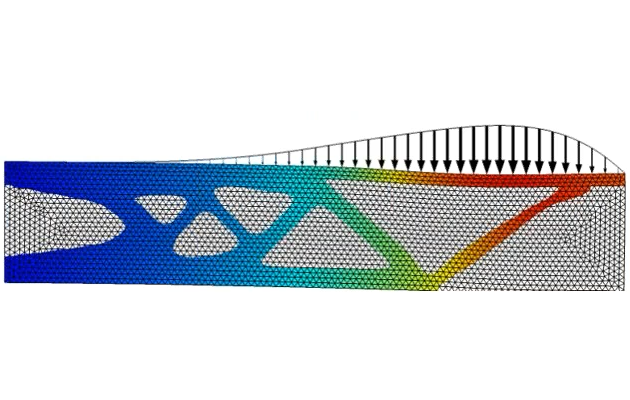
We also talk about the importance of regularization in shape optimization and how the features listed here regularize the shape changes of the geometry in a model. Following this, we continue with the beam tutorial model, which we previously solved using parametric optimization, but will now solve with shape optimization. The Shape Optimization interface is used to specify which boundaries can be optimized, which boundaries are fixed, and which (straight) boundaries can change length but not orientation. We encourage you to download the cleared model file and follow along with the demonstration. After computing the model, we talk about the advantages of using gradient-based optimization and how to avoid common problems.
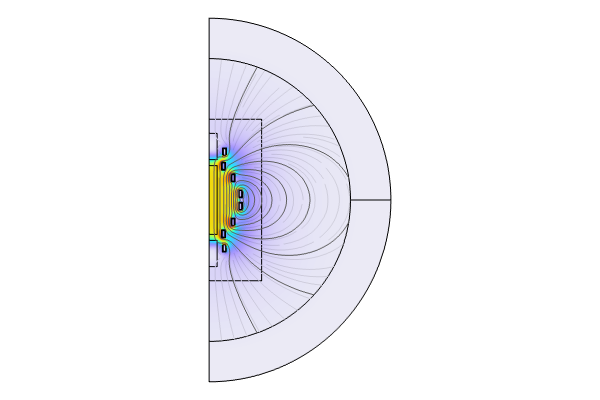
We then move on to a second model example, with which we demonstrate performing shape optimization to optimize the band dispersion in an electroosmotic flow through a curved microchannel. We discuss and show the different approaches we could use to solve this problem as well as the respective objective functions we would formulate for each approach. Toward the end of the presentation, we highlight related blog posts and tutorial models for further learning.
Submit feedback about this page or contact support here.