Hydrocarbon Dehalogenation in a Tortuous Microreactor
Application ID: 2182
Removing halogen groups from hydrocarbons is an important reaction step in several chemical processes. One application is water purification. Other examples involve organic synthesis, where the removal of halogen groups serves as a starting point for carbon-carbon coupling reactions. Typically, the carbon-halogen bond scission is activated by precious metal catalysts based on platinum or palladium.
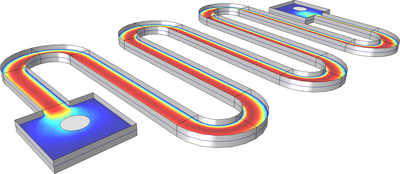
This model shows hydrocarbon dehalogenation as it occurs in a microreactor. The reactants are transported from the fluid bulk to the catalytic surfaces at the reactor walls, where they react. First you set up a space-independent model, analyzing two competing reactions, using the Reaction Engineering interface. Then, you export the reaction kinetics and set up and solve a space-dependent model of the microreactor.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- either the Chemical Reaction Engineering Module, or Electric Discharge Module and
- either the Battery Design Module, CFD Module, Chemical Reaction Engineering Module, Corrosion Module, Electrochemistry Module, Electrodeposition Module, Fuel Cell & Electrolyzer Module, Microfluidics Module, Polymer Flow Module, Porous Media Flow Module, or Subsurface Flow Module
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



