Cross-Section Analysis
In COMSOL Multiphysics®, you can calculate the cross sections of the scatterer in your optical scattering applications. In this article, we will demonstrate this process, in which we continue to build upon the base application built at the start of the course.
Tutorial: Calculating the Scatterer Cross Sections
Follow along in the software using the completed model built in Part 1 (the optical scattering off a gold nanosphere) as we demonstrate how to calculate the scattering, absorption, and extinction cross sections. Important steps in building the model include understanding the cross-section definitions, defining variables to calculate the cross sections, and analyzing wavelength dependence. These steps are highlighted after the tutorial.
Note: This process is automated with the Cross Section Calculation feature available in COMSOL Multiphysics version 6.3, which is demonstrated in the Scatterer on Substrate and Optical Scattering of a Gold Nanosphere tutorial models. Learn more here.
Cross-Section Definitions
The scattering cross section is defined as:
.
Here, is the normal vector pointing outward from the scatterer,
is the scattered intensity (Poynting) vector, and
is the incident intensity. The integral is taken over the closed surface of the scatterer.
The absorption cross section equals
,
where is the power loss density in the particle, and the integral is taken over its volume. The extinction cross section is simply the sum of the scattering and absorption:
.
Cross Sections in COMSOL Multiphysics
To calculate the cross sections of our scatterer, we add new variables to our existing base application. The corresponding variables and integrals are defined as follows.
 The Model Builder with the Variables node selected and the corresponding Settings window.
The Model Builder with the Variables node selected and the corresponding Settings window.
The variables defined for calculating the scattering, absorption, and extinction cross sections. Integration coupling operators are defined and used in the expression for some variables.
Note that the default electric field strength of the background field, E0 (1 [V/m]), used in the intensity calculation can easily be replaced as needed.
Wavelength Range
To obtain the wavelength-dependent cross-section data, a wavelength range is added to the Wavelength Domain study starting at lam_min (value of 400 nm).

The range specified in the Wavelength Domain study step.
Wavelength Dependence
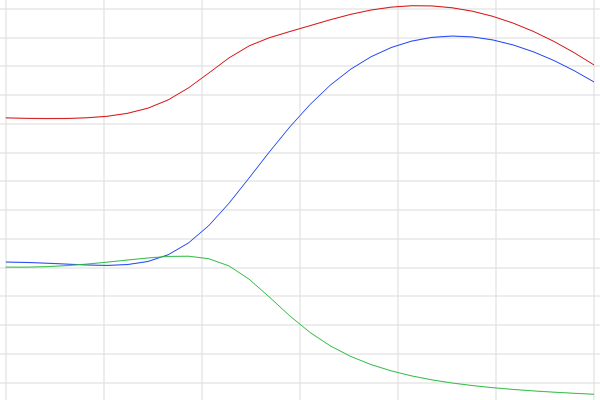
To visualize the wavelength dependence, a Global Plot is used that contains lines for each of the variables defined for the scattering, absorption, and extinction cross sections.
 A line graph showing a red, blue, and green line for the scattering, absorption, and extinction cross sections.
A line graph showing a red, blue, and green line for the scattering, absorption, and extinction cross sections.
The results for the wavelength dependence on the cross-section calculations after computing the model.
Depending on the size and resolution of the spectral sweep, the calculations can become fairly demanding, leading us to the next part of this course.
Further Learning
For more information on the theoretical background regarding the cross sections, see the documentation for the Scatterer on Substrate tutorial model.
Submit feedback about this page or contact support here.