Composite Materials Module Updates
New Microstructure Geometry Parts
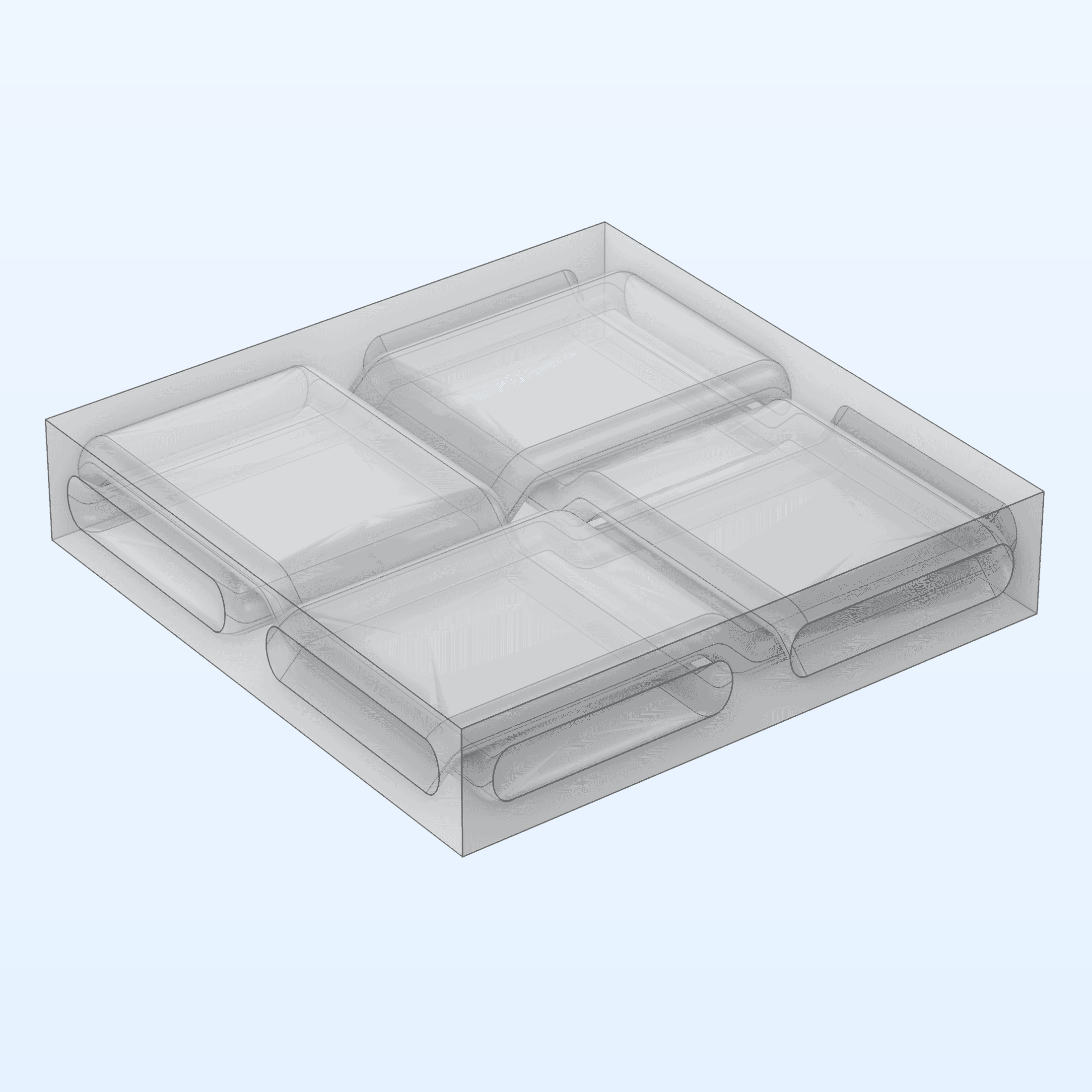
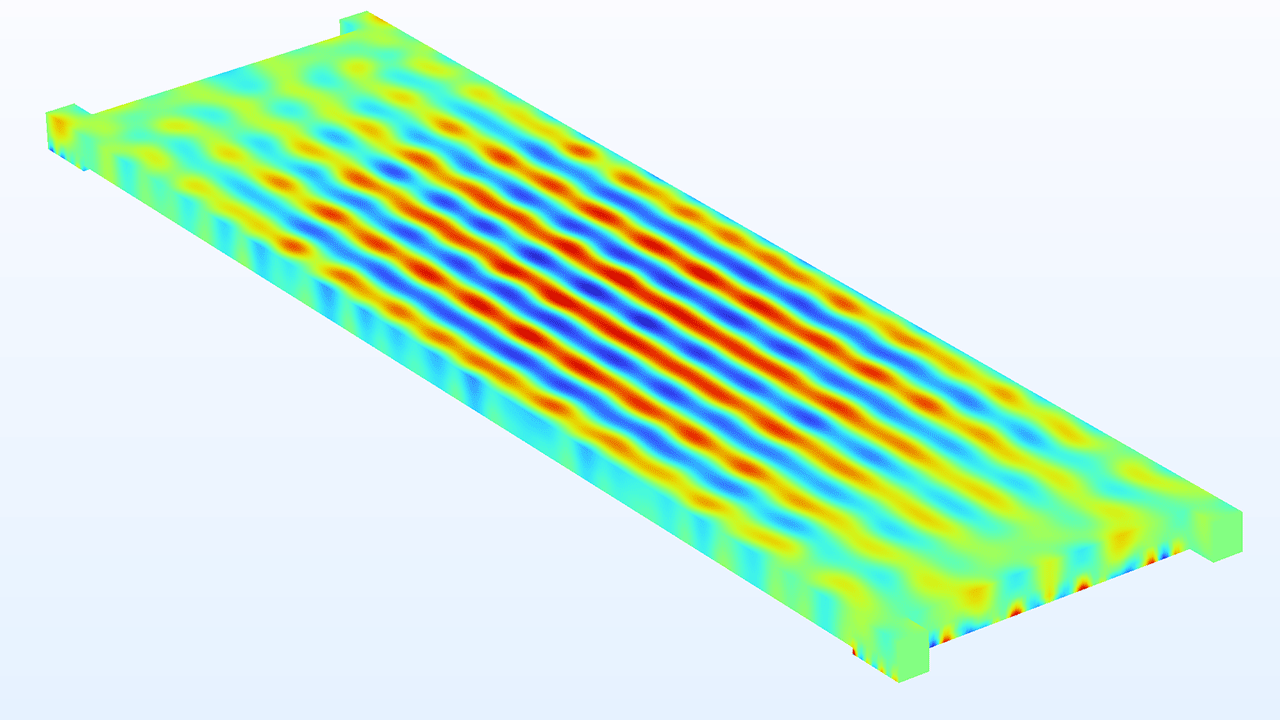
A new microstructure geometry part for bidirectional spread-tow fiber composites is now available. This part features a unit cell with fiber strands arranged in a plain weave, embedded within a matrix. You can find it in the Part Libraries under the COMSOL Multiphysics branch, within the Unit Cells and RVEs folder. This part is showcased in the Dome Tweeter with Composite Diaphragm — Eigenfrequency Analysis tutorial model.
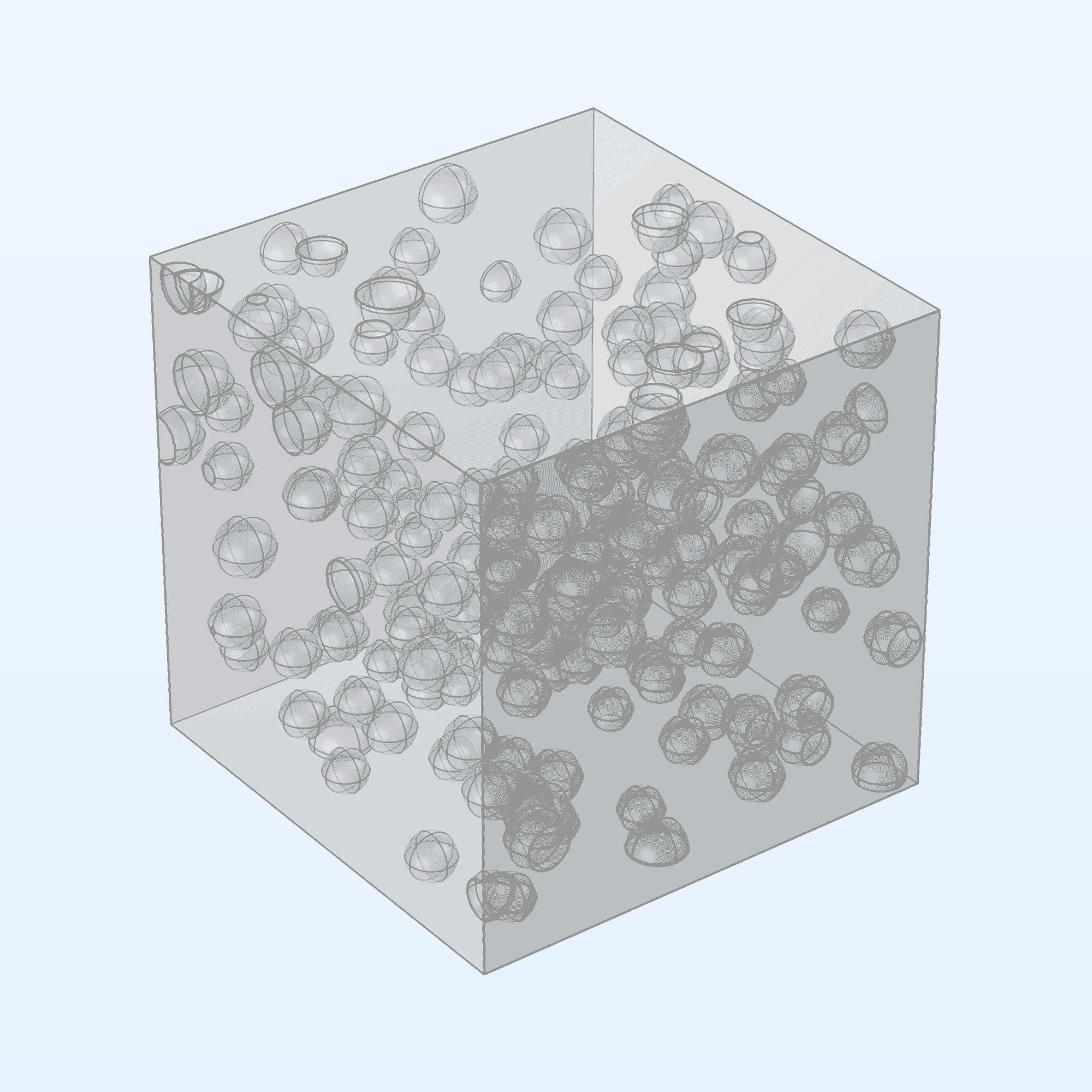
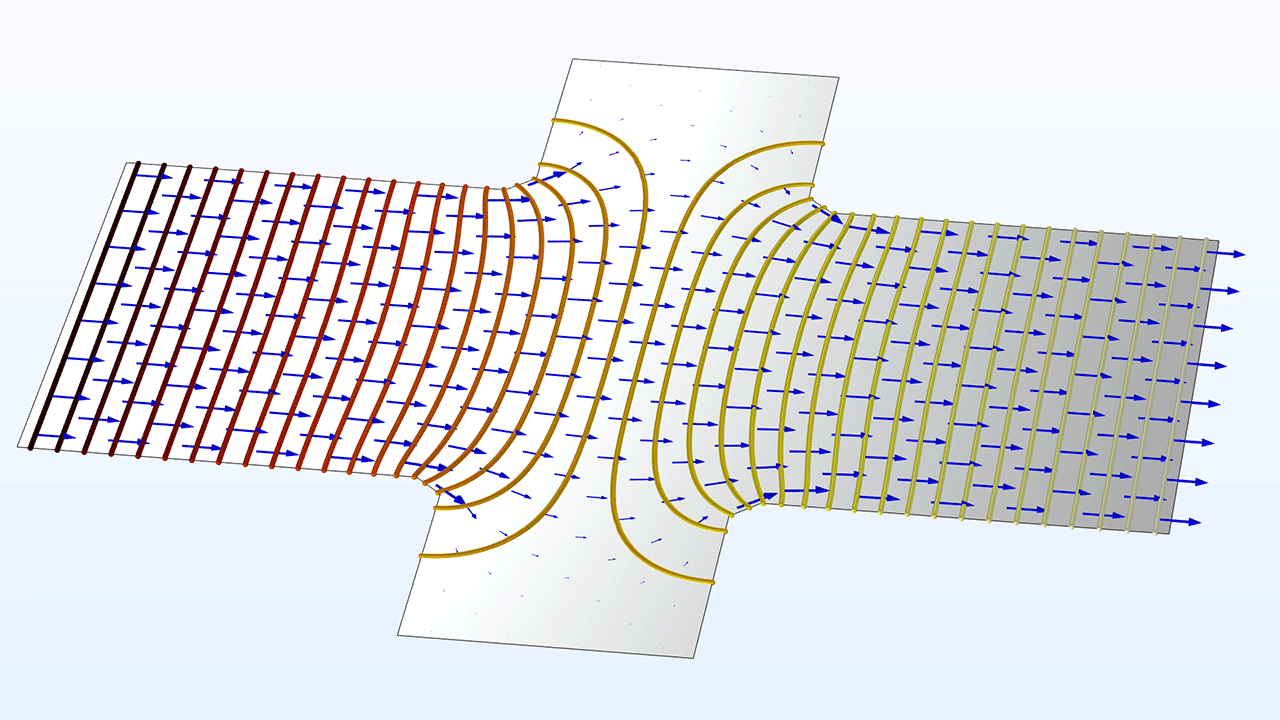
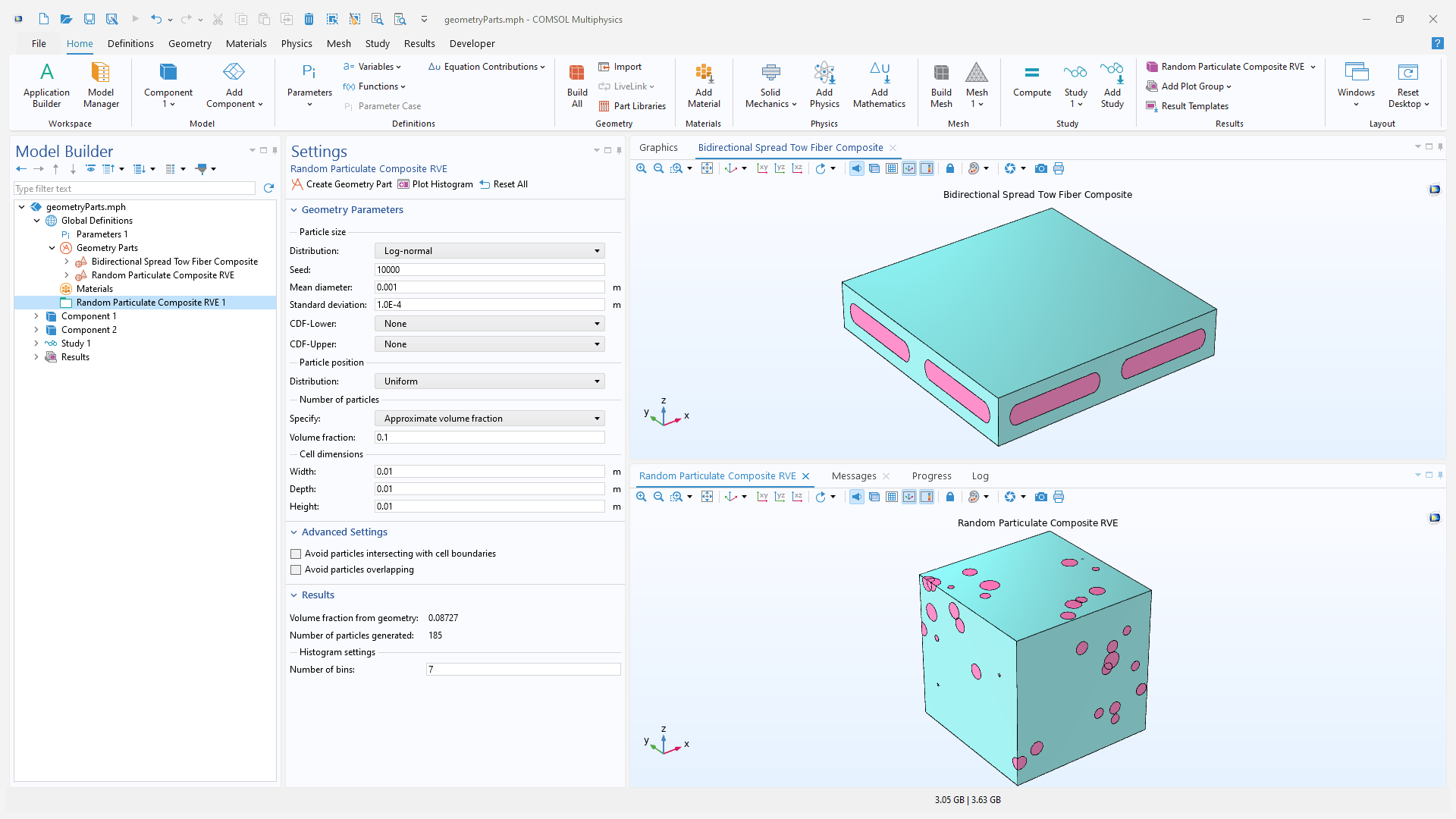
Additionally, a new add-in to generate geometry parts for random-particulate composites has been added under the COMSOL Multiphysics branch of the Add-in Libraries window.
The new bidirectional spread-tow fiber composite geometry part (left) and a random-particulate composite geometry part generated by the add-in (right).
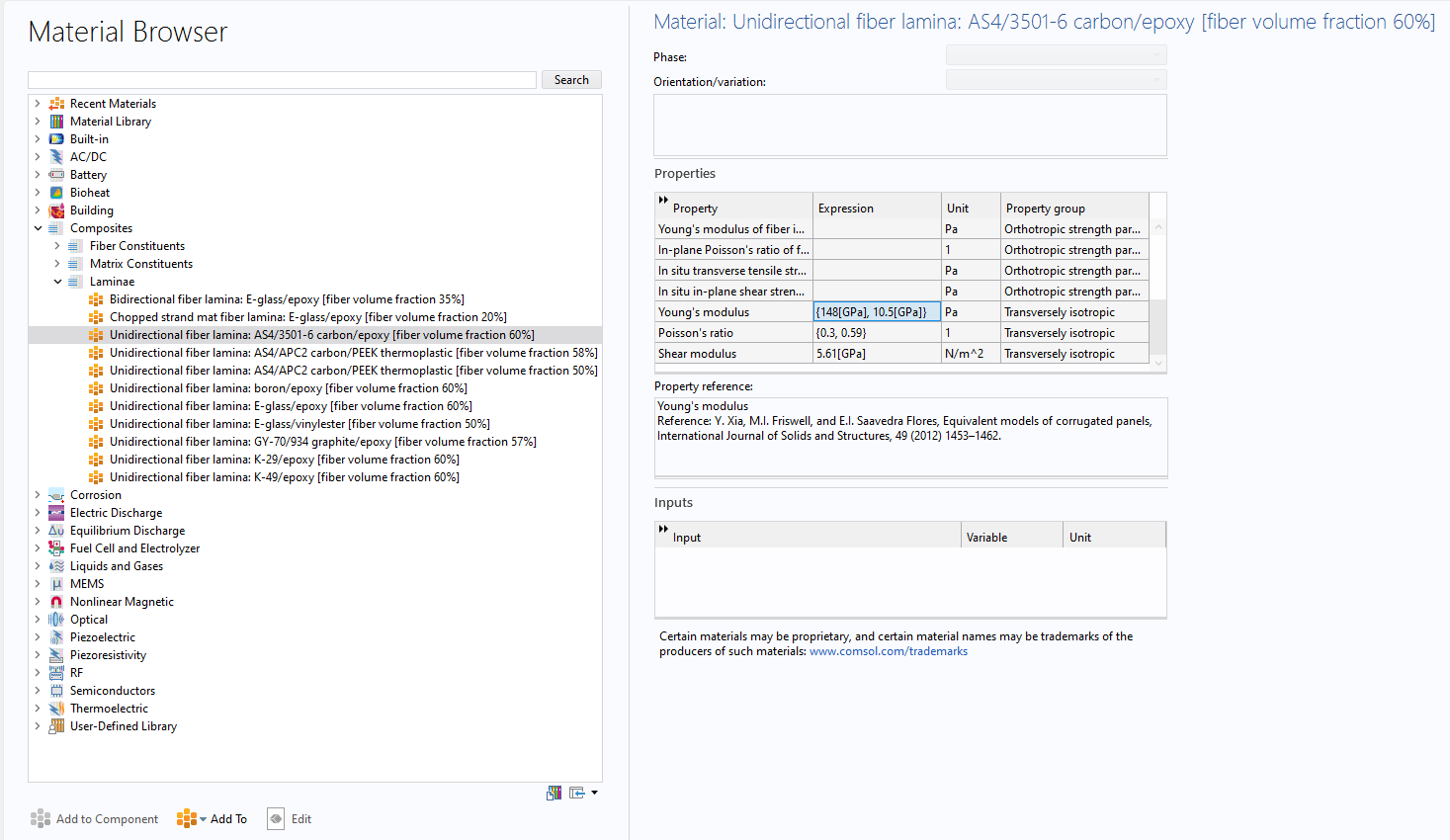
Composites Material Library Folder
The new built-in folder for Composites is divided into three groups of materials: fiber constituents, matrix constituents, and laminae. This functionality makes it easier to set up models with common types of composite plies. You can view these new materials being used in the following tutorial models:
- composite_dome_tweeter_eigen (new)
- composite_cylinder_micromechanics_and_stress_analysis
- composite_multiscale
- composite_wheel_rim
- ply_drop_off_in_a_composite_panel
- layered_shell_structure_connection
- stacking_sequence_optimization
- progressive_delamination_in_a_laminated_shell
- homogenization_of_periodic_microstructures
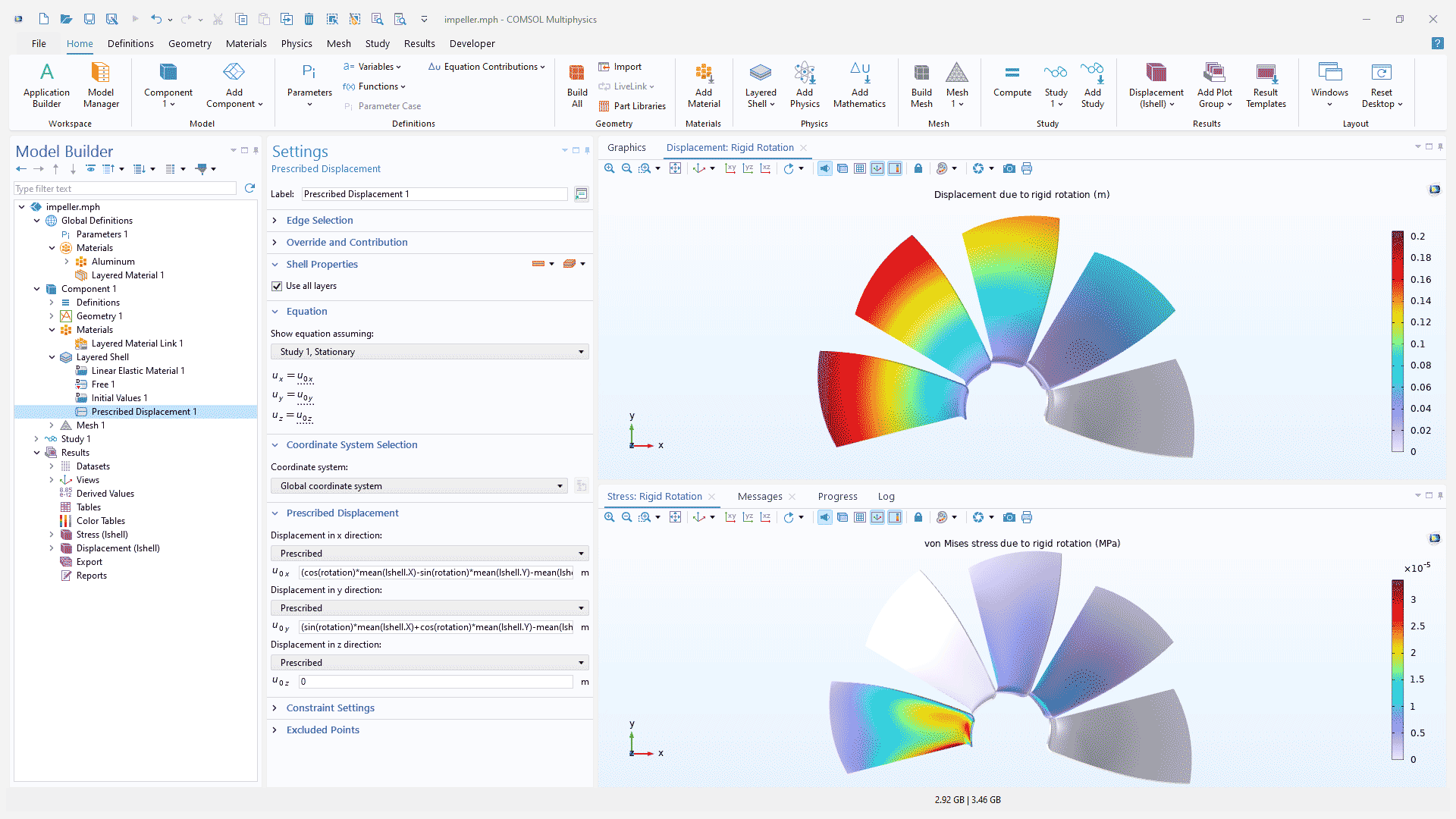
Layered Shell Interface Improvements
There are four main improvements to the Layered Shell interface:
The kinematics has been improved to account for large deformations.
A new coordinate system, Layer Local System, has been added to several physics features.
Solver suggestions for multiphysics problems have been improved.
The Creep, Viscoplasticity, and Polymer Viscoplasticity material models can now be used together with hyperelastic material models.
- Note that the Creep, Viscoplasticity, and Polymer Viscoplasticity material models require the Nonlinear Structural Materials Module.
New Tutorial Models
COMSOL Multiphysics® version 6.3 brings several new tutorial models to the Composite Materials Module.
Dome Tweeter with Composite Diaphragm — Eigenfrequency Analysis
Dome Tweeter with Composite Diaphragm — Frequency-Domain Response*
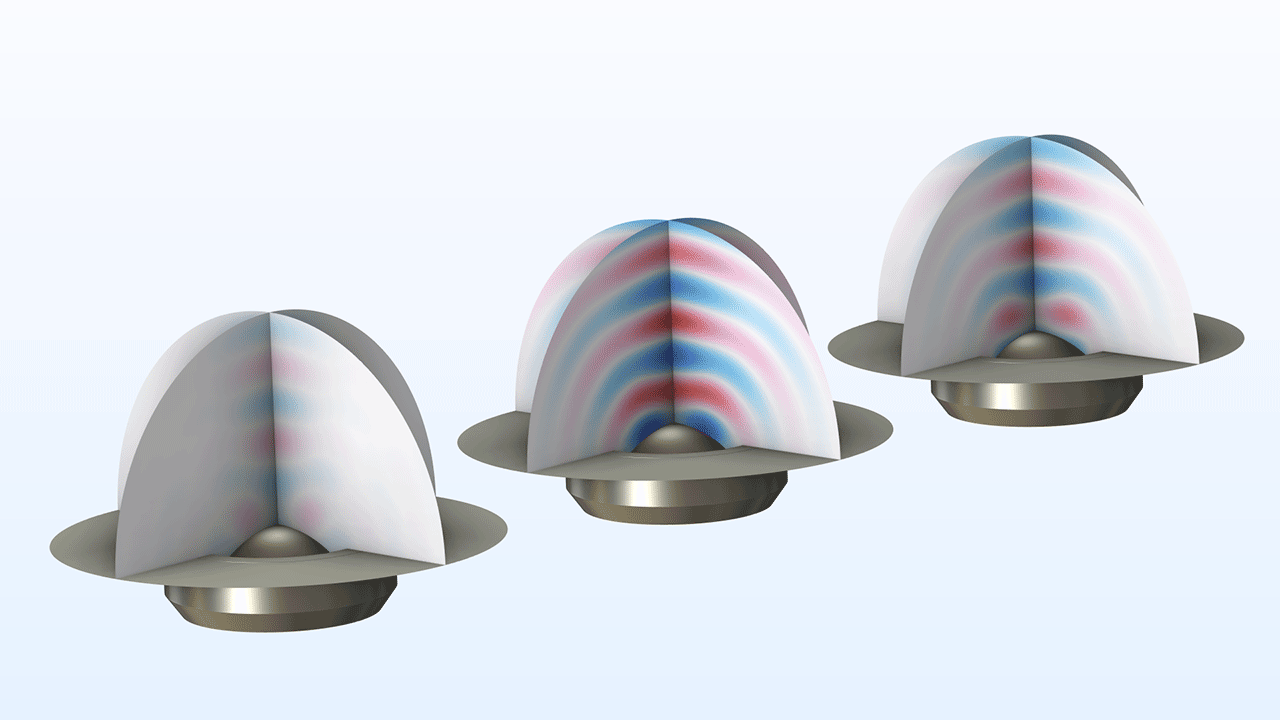
Application Library Title:
dome_tweeter_composite_63
Download from the Application Gallery
*Requires the Acoustics Module
Aluminum Nitride Lamb Wave Resonator — Layered Shell Version*
Application Library Title:
aln_lamb_wave_resonator_layered
Download from the Application Gallery
*Requires the MEMS Module
Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor — Layered Shell Version*
Application Library Title:
piezoresistive_pressure_sensor_layered
Download from the Application Gallery
*Requires the MEMS Module