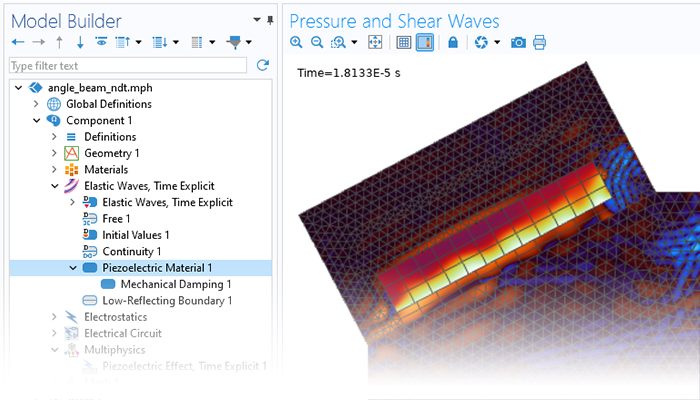
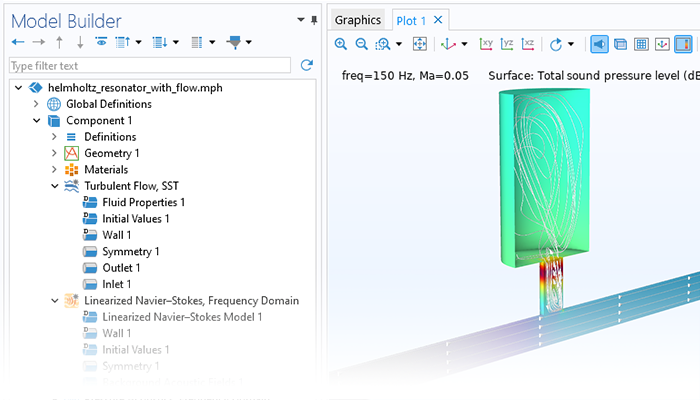
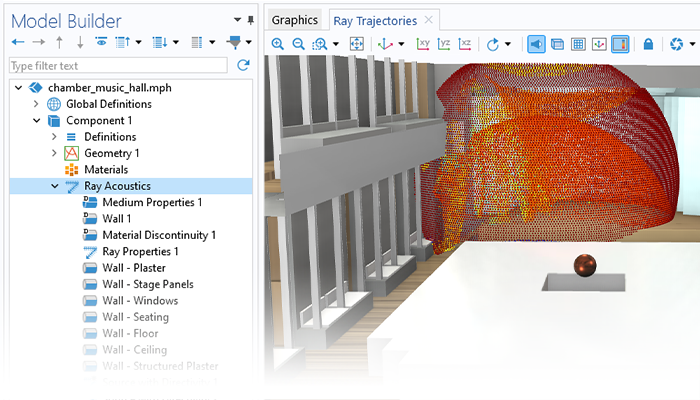
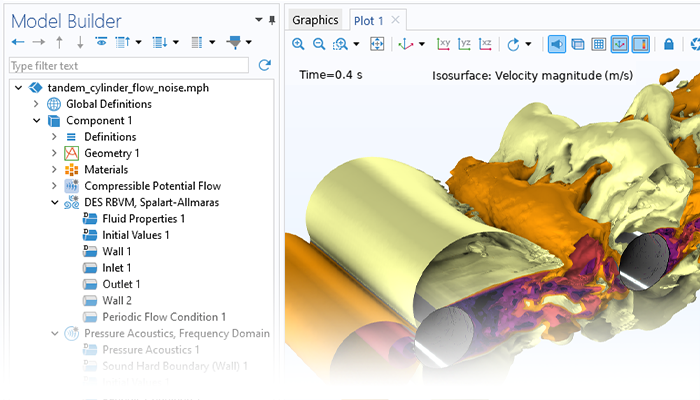
Pressure Acoustics
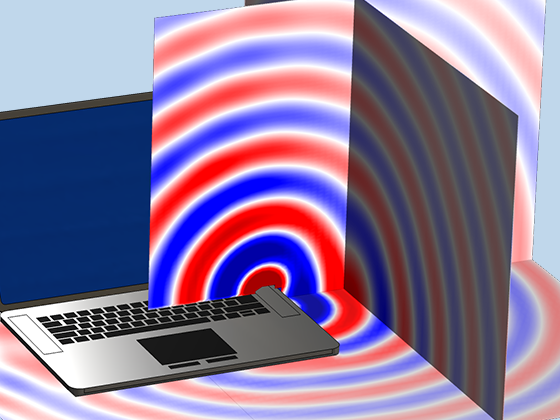
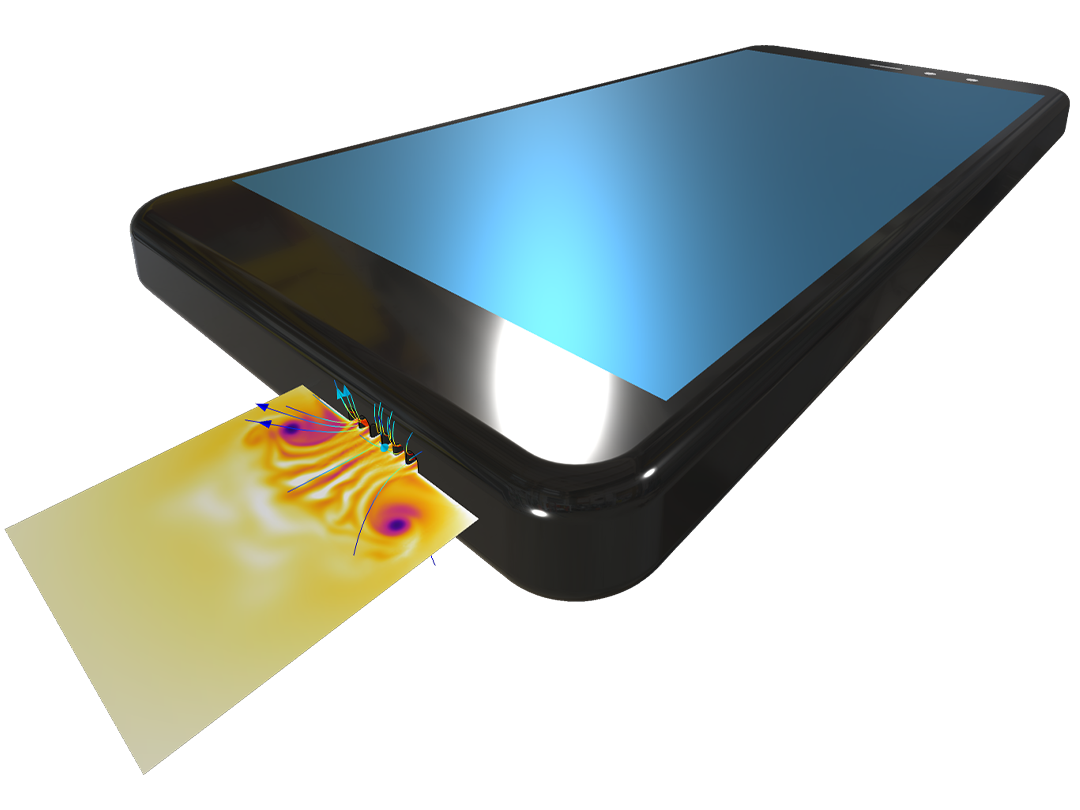
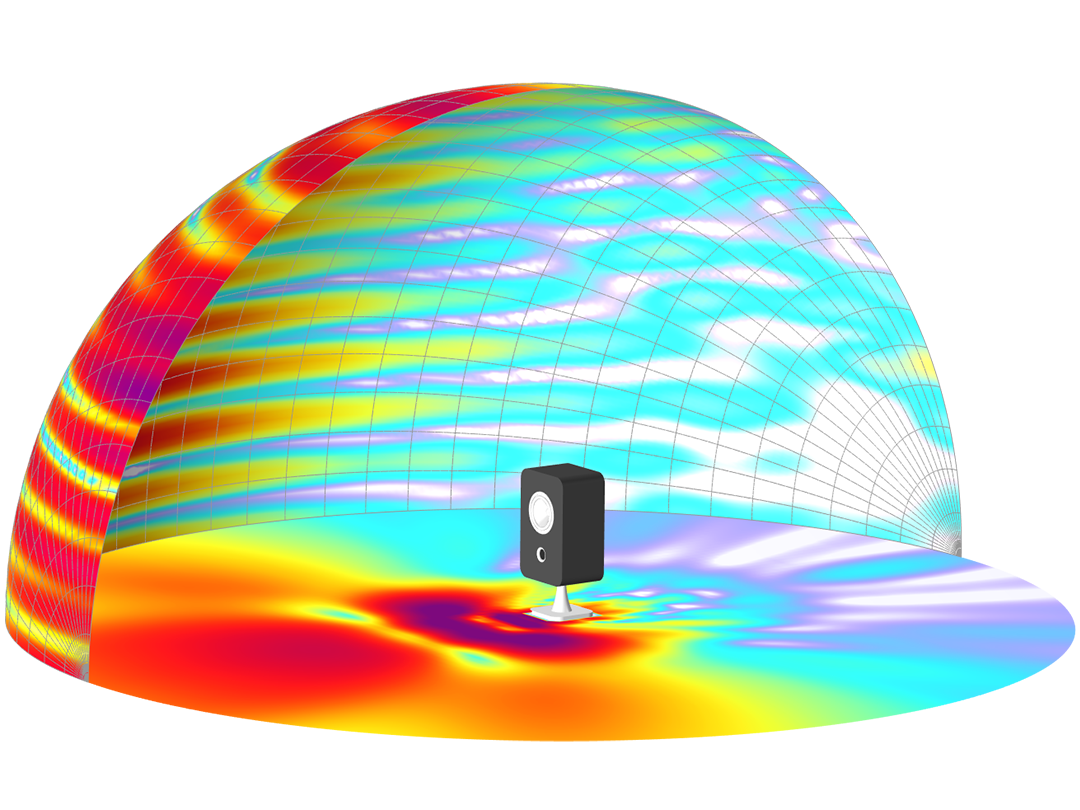
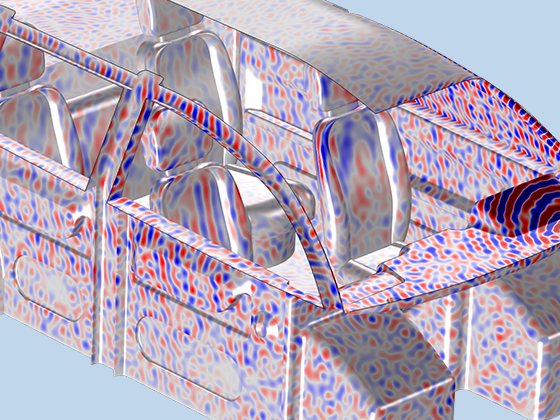
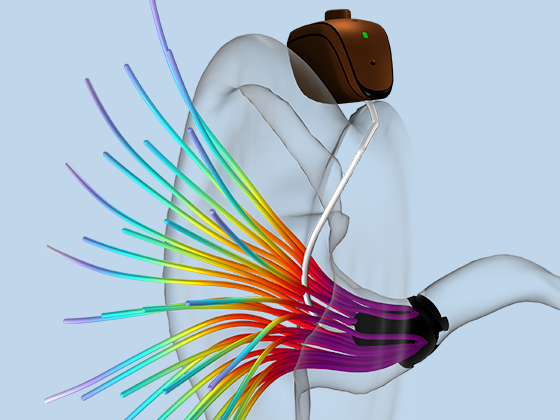
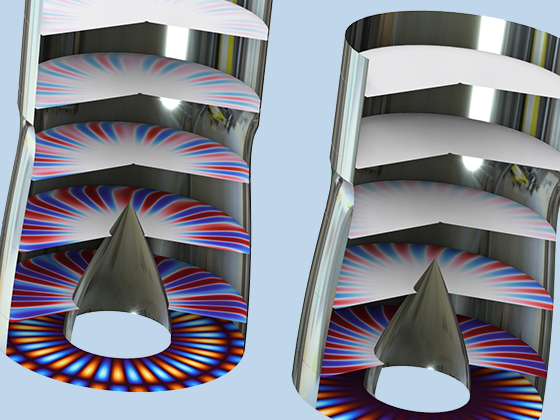
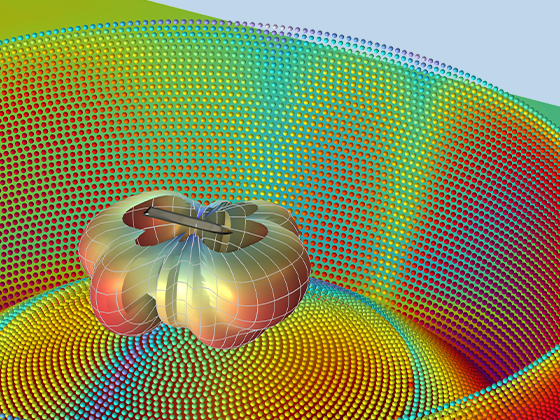
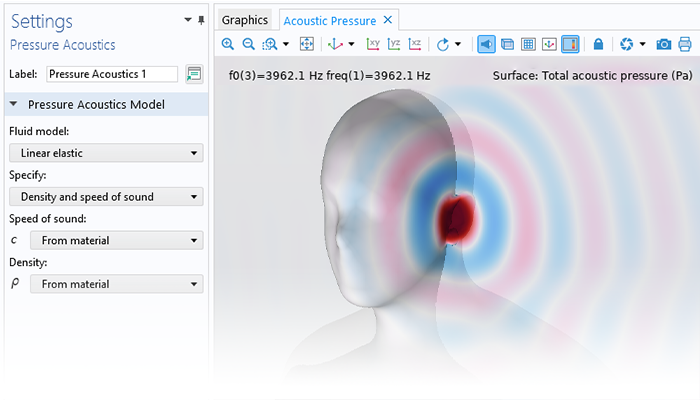
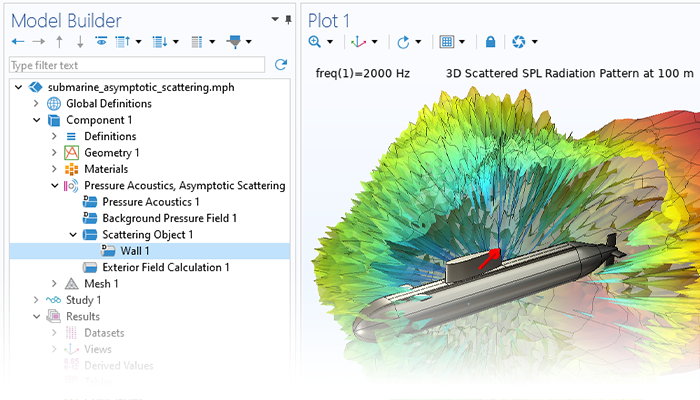
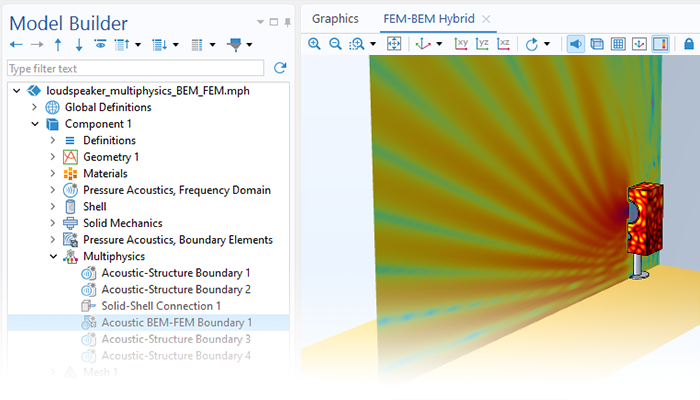
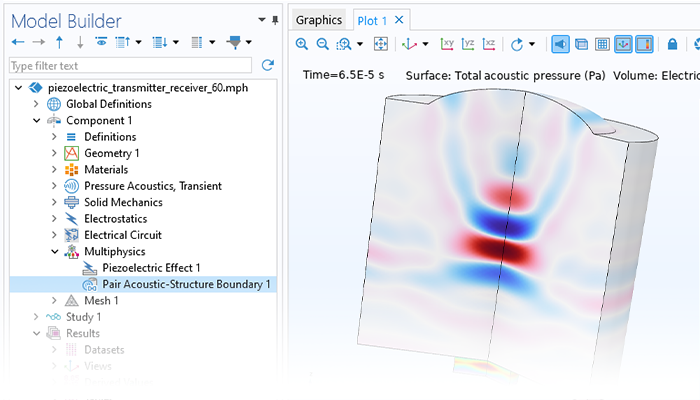
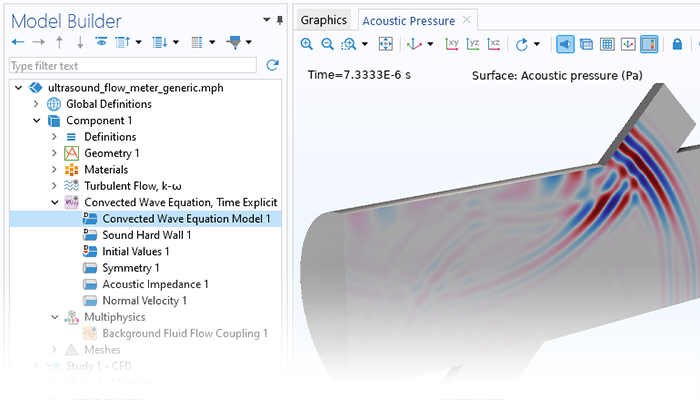
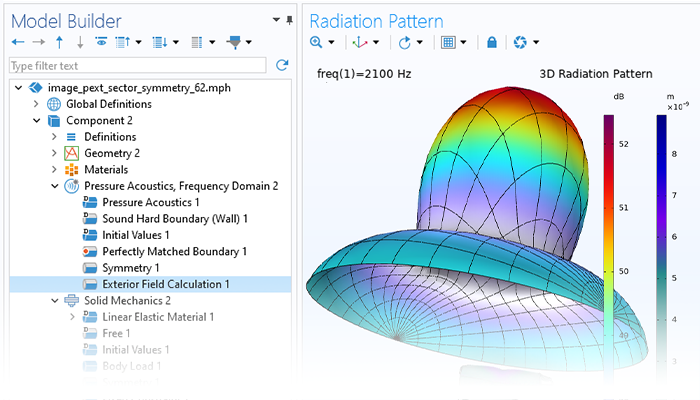
Modeling pressure acoustics is the most common use of the Acoustics Module. It includes capabilities for modeling effects such as the scattering, diffraction, emission, radiation, and transmission of sound. Simulations run in the frequency domain employ the Helmholtz equation, whereas in the time domain, the classical scalar wave equation is used. In the frequency domain, both FEM and BEM are available, as well as hybrid FEM–BEM. In the time domain, time implicit (FEM) as well as time explicit (dG-FEM) formulations are available.
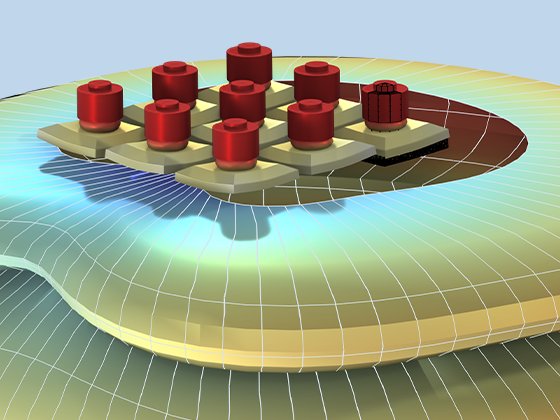
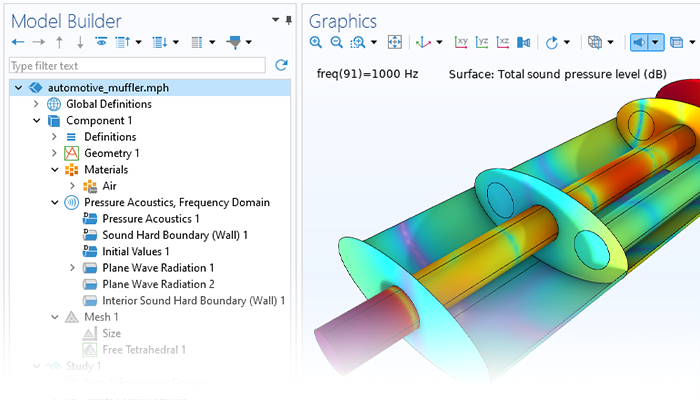
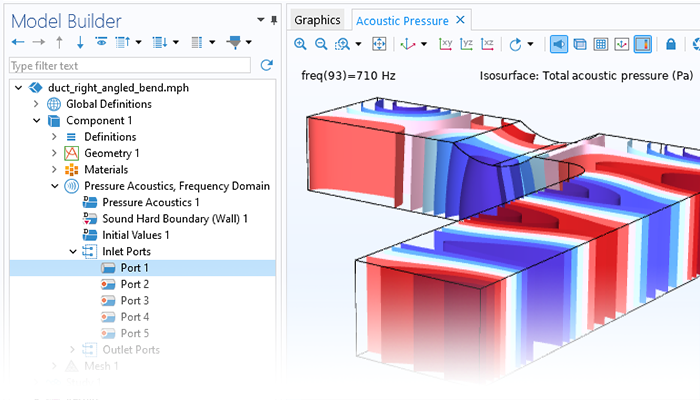
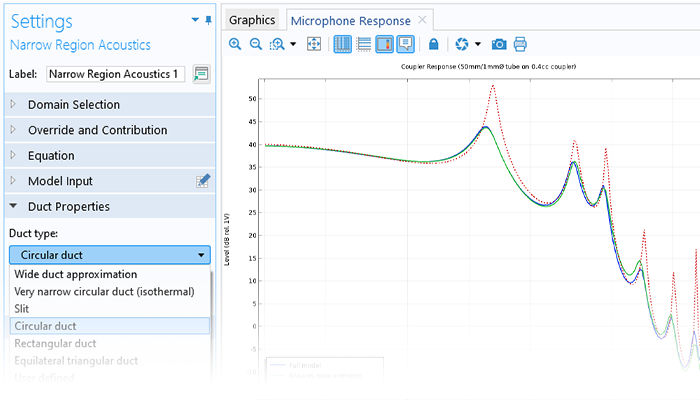
There are many options to account for boundaries in acoustics models. For instance, a boundary condition can be added for a wall, or an impedance condition can be added for a porous layer. Ports can be used to excite or absorb acoustic waves at the inlet and outlet of waveguide structures using multimode expansion. This applies to ducts, periodic structures, or boundary couplings to lumped acoustic models. Sources like prescribed acceleration, velocity, displacement, or pressure can be applied on exterior or interior boundaries. Furthermore, radiation or Floquet periodic boundary conditions can be used to model open or periodic boundaries.
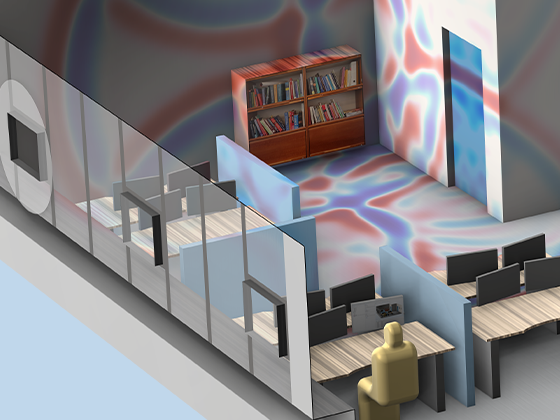
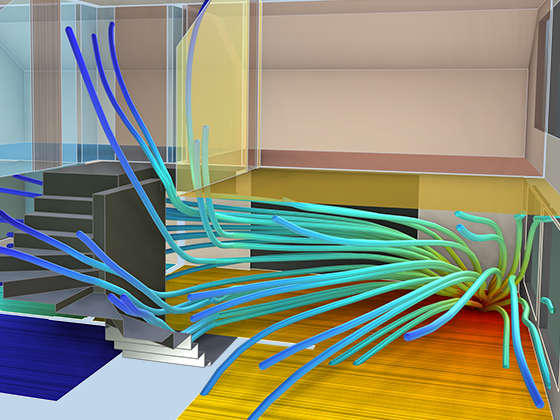
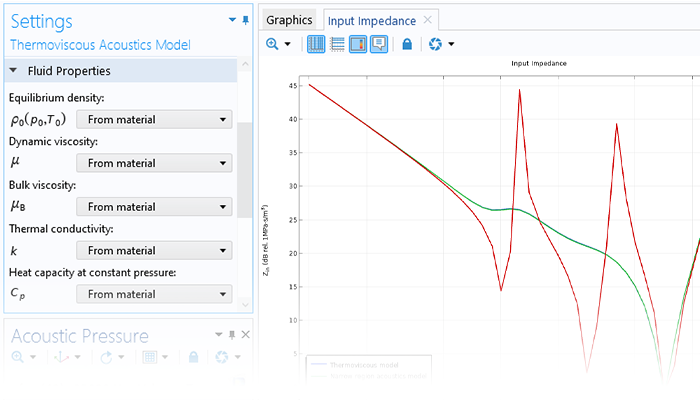
The dG-FEM time-domain-based formulation can be run on a GPU for increased performance in, for example, wave-based room acoustic simulation scenarios. Time-domain simulations are further enhanced with dedicated tools for including general frequency-dependent impedance conditions and porous material data.
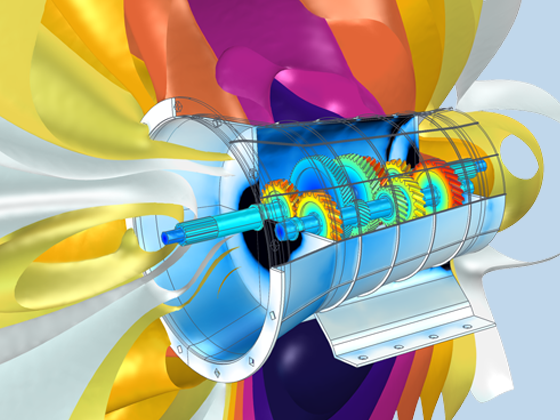
The Acoustics Module can also be used to model pipe acoustics, computing the acoustic pressure and velocity in flexible pipe systems. Applications include HVAC systems, large piping systems, and musical instrument components such as organ pipes.